对象与方法
一、研究对象与分组
二、方法
三、统计学处理
结果
一、无冠心病组、PCAD组与晚发冠心病组各临床指标比较
表1 无冠心病组、PCAD组与晚发冠心病组的各临床指标比较 |
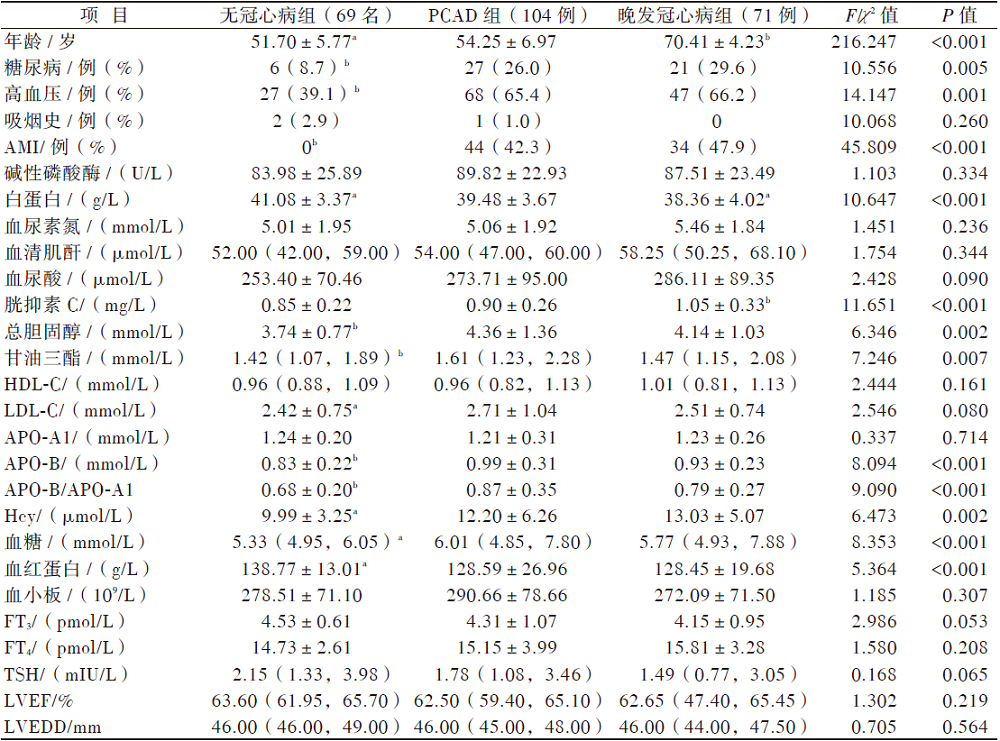 |
注:与PCAD组比较,aP < 0.05,bP < 0.001。 |

喀什地区女性早发冠心病的危险因素分析
Copy editor: 杨江瑜
收稿日期: 2022-06-16
网络出版日期: 2022-12-02
基金资助
新疆维吾尔自治区自然科学基金(2018D01C020)
广东省援疆科技(特派员)项目(KTP202033)
Risk factors of premature coronary artery disease in women in Kashgar area
Received date: 2022-06-16
Online published: 2022-12-02
目的 分析以维吾尔族居民为主的喀什地区女性早发冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病(PCAD)的危险因素,为该地区有效防治女性PCAD提供依据。方法 选择住院行冠状动脉造影的喀什地区维吾尔族女性244名,根据冠状动脉造影(CAG)结果和年龄分为3组:无冠心病组(69名)、PCAD组(104例)和晚发冠心病组(71 例),比较3组患者的临床资料。采用单因素、多因素logistic回归分析PCAD的危险因素。结果 PCAD组年龄 (54.25±6.97)岁,其中因AMI就诊达42.3%,且在冠心病患者中占比高达59.4%。与无冠心病组相比,PCAD组患高血压、糖尿病比例更高,且总胆固醇、甘油三酯、载脂蛋白(APO)-B、同型半胱氨酸(Hcy)及血糖水平均更高,而白蛋白、血红蛋白均更低,比较差异均有统计学意义(P均< 0.05);但与晚发冠心病组相比,PCAD组除胱抑素C水平较低,白蛋白、APO-B较高外,2组其余指标比较差异均无统计学意义(P均> 0.05)。多因素logistic回归分析结果显示,PCAD的独立危险因素包括:糖尿病[OR=4.349,95%CI(1.411,13.402)]、高血压[OR=3.121,95%CI (1.467,6.639)]、APO-B/APO-A1[OR=5.603,95%CI(1.128,27.838)]、Hcy[OR=1.188,95%CI(1.070,1.318)]。结论 喀什地区女性冠心病患者在65岁之前发病较为常见,且糖尿病、高血压、高APO-B/APO-A1值、高Hcy水平是PCAD的独立危险因素,应早期筛查并干预。
赵小丽 , 田云涛 , 提拉柯孜·图尔荪 , 胡育英 , 杨和银 , 钱孝贤 , 谢旭晶 . 喀什地区女性早发冠心病的危险因素分析[J]. 新医学, 2022 , 53(11) : 810 -814 . DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9802.2022.11.005
Objective To identify the risk factors of women with premature coronary artery disease (PCAD) in the Kashgar area, mainly Uyghur residents, providing evidence for effective prevention and treatment of PCAD in this region. Methods Two hundred and forty-four Uighur females in Kashgar area who were hospitalized for coronary angiography (CAG) were enrolled. According to the results of CAG and ages, they were divided into three groups: 69 cases in the control group, 104 cases in the PCAD group, and 71 cases in the late-onset coronary artery disease group. Clinical data were compared among three groups. Univariate and multivariable logistic regression analyses were used to identify the risk factors of PCAD. Results The mean age of onset in the PCAD group was (54.25±6.97) years, and 42.3% of them were admitted due to AMI, accounting for 59.4% in patients with coronary heart disease. Compared with the control group, patients with PCAD had higher prevalence of hypertension and diabetes mellitus, and higher levels of CHOL, TG, APO-B, Hcy and GLU, whereas lower levels of ALB and HGB (all P < 0.05), while compared with the late-onset coronary artery disease group, PCAD group had a lower level of Cys-C, but higher levels of ALB and APO-B, and there was no significant difference in other indicators between two groups (all P > 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that diabetes mellitus [OR = 4.349, 95%CI(1.411, 13.402)], hypertension [OR = 3.121, 95%CI(1.467, 6.639)], APO-B/APO-A1 ratio [OR = 5.603, 95%CI(1.128, 27.838)], Hcy [OR =1.188, 95%CI(1.070, 1.318)] were the independent risk factors of PCAD. Conclusions The onset of coronary heart disease is relatively common in female patients aged < 65 years. Diabetes mellitus, hypertension, high APO-B/APO-A1 ratio and high Hcy level are the independent risk factors for women with PCAD in Kashgar area. Early screening and intervention are needed to prevent PCAD in Kashgar area.
Key words: Kashgar area; Female; Premature coronary artery disease; Risk factor
表1 无冠心病组、PCAD组与晚发冠心病组的各临床指标比较 |
 |
注:与PCAD组比较,aP < 0.05,bP < 0.001。 |
| [1] |
中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组. 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2020概要. 中国循环杂志, 2021, 36(6):521-545.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
Atlas Writing Group; ESC Atlas of Cardiology is a compendium of cardiovascular statistics compiled by the European Heart Agency, a department of the European Society of Cardiology; Developed in collaboration with the national societies of the European Society of Cardiology member countries, et al. European Society of Cardiology: Cardiovascular Disease Statistics 2019 (Executive Summary). Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes, 2020, 6(1):7-9.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
金梅花, 张波涛, 张辉, 等. 宁夏地区早发冠心病患者危险因素及冠状动脉病变特点. 宁夏医科大学学报, 2018, 40(6): 706-709.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
Authors/Task Force Members, ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG), ESC National Cardiac Societies. 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Atherosclerosis, 2019, 290:140-205.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
马晓佳. 新疆喀什地区维吾尔族高血压流行及控制现状调查分析. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2013.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
王福英, 夏大胜, 郭倩玉, 等. 血清瘦素与早发冠心病及凝血因子Ⅶ的关系. 新医学, 2012, 43(11):764-768.
|
| [17] |
孙珂, 许梦情, 王晓军, 等. 新疆贫困地区维吾尔族农民肥胖与血脂异常相关性. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2020, 36(1):71-78.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |