 PDF(4966 KB)
PDF(4966 KB)


 PDF(4966 KB)
PDF(4966 KB)
 PDF(4966 KB)
PDF(4966 KB)
椎间孔镜通道导向模块在椎间孔镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症中的应用
Clinical application of transforaminal endoscope-guided module in treatment of lumbar disc herniation by transforaminal endoscopic
目的 探讨椎间孔镜通道导向模块在椎间孔镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症中的应用价值。方法 选取60例L5/S1腰椎间盘突出症患者,将其随机分为模块组和对照组各30例。模块组采用一种自创的椎间孔镜通道导向模块辅助穿刺,对照组采用传统徒手穿刺放置工作管道。比较2组的一次穿刺成功率、定位穿刺时间和术中X线透视次数,观察并发症发生情况,比较2组术后3个月的视觉模拟评分法(VAS)评分、臀部和下肢功能障碍指数(ODI)评分,并采用改良Mac Nab评分评估2组疗效。结果 2组患者术程均顺利。与对照组比较,模块组一次穿刺成功率更高、穿刺时间更短、术中X线透视次数更少(P均< 0.05)。2组患者术中并发症发生率比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),术后均无出现严重并发症。2组患者术后3个月的VAS评分与ODI评分均较术前降低(P均< 0.01),模块组与对照组术后3个月的VAS、ODI评分比较差异均无统计学意义(P均> 0.05),但2组VAS术前术后评分差值比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。模块组改良Mac Nab评分优良率为83.3%(25/30),对照组优良率为80.0%(24/30),2组比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。结论 在椎间孔镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症中,椎间孔镜通道导向模块操作简便且安全,可以缩短穿刺时间、提高穿刺效率、减少医源性损伤,值得在临床进一步推广应用。
Objective To evaluate the clinical application value of transforaminal endoscope-guided module in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation by transforaminal endoscopic. Methods Sixty patients with L5 / S1 lumbar disc herniation were randomly divided into the module group and control group, with 30 cases in each group. In the module group, self-designed transforaminal endoscope-guided module was utilized to assist puncture, and conventional manual puncture was adopted to place the working channel in control group. The success rate of one-time puncture, positioning puncture time and intraoperative X-ray fluoroscopy times were compared between two groups, and the incidence of complications was observed. The Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) score and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) score of the hip and lower limbs at postoperative 3 months were compared between two groups. Postoperative modified Mac Nab score was employed to evaluate clinical efficacy between two groups. Results All patients successfully completed the operation. Compared with the control group, the success rate of one-time puncture was higher, positioning puncture time was shorter and the times of intraoperative X-ray fluoroscopy was less in the module group (all P <0.05). There was no statistical significance in the incidence of intraoperative complications between two groups (P >0.05), and no severe postoperative complications were noted in two groups. In two groups, the VAS score and ODI score at postoperative 3 months were less compared with preoperative levels (both P <0.05), and there was no statistical significance between two groups (both P >0.05),however, the difference of VAS between preoperative and postoperative values was statistically significant(P <0.05). There was no statistical significance in the excellent rate of modified Mac Nab score between the module (83.3% (25/30))and control groups (80.0% (24/30), P >0.05). Conclusions Transforaminal endoscope-guided module is safe and convenient. This module can effectively shorten puncture time, enhance puncture efficiency and minimize iatrogenic injuries, which is worthy of clinical application.
椎间孔镜通道导向模块 / 经皮椎间孔镜椎间盘切除术 / 辅助穿刺装置 / 腰椎间盘突出症 / 经椎间孔入路 {{custom_keyword}} /
Transforaminal endoscope-guided module / Percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy / Auxiliary puncture device / Lumbar disc herniation / Transforaminal route {{custom_keyword}} /
表1 模块组与对照组LDH患者一般资料比较Table 1 Comparison of general data of LDH patients in the module group and the control group |
| 分 组 | n | 男/女 | 年龄/岁 | 病程/月 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模块组 | 30 | 13/17 | 44.0(35.5,52.3) | 15.5(10.8,20.3) |
| 对照组 | 30 | 16/14 | 39.0(24.5,47.5) | 16.0(12.8,22.0) |
| Z值 | 0.601 | 1.902 | 0.681 | |
| P值 | 0.438 | 0.086 | 0.498 |
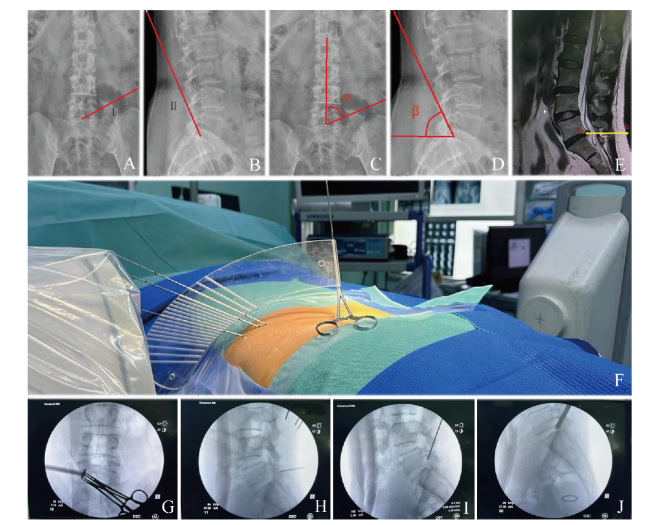
图2 应用椎间孔镜通道导向模块的操作图例注:A~D为腰椎X线片,A中红线为穿刺基线Ⅰ(由上关节突尖部到后正中线距离);B中红线为穿刺基线Ⅱ(由上关节突尖部到下位椎体后上角);C为外展角α;D为头倾角β;E为MRI片上确定穿刺定位针穿刺深度(a点到b点距离);F为根据术前预设方位摆放椎间孔镜通道导向模块;G~J为C型臂机X线片,G、H为确定放置克氏针方位;I为选择最佳穿刺方向后进针到位;J为靶向穿刺置管到位。Figure 2 Illustrates the operation of the foraminal mirror channel guide module |
表2 模块组与对照组穿刺情况比较Table 2 Comparison of puncture conditions between the module group and the control group |
| 组 别 | 一次穿刺成功/n(%) | 穿刺时间/min | 术中C型臂机X线透视次数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 模块组(n=30) | 17(68.0) | 5.0(4.0,6.0) | 11.0(10.0,12.0) |
| 对照组(n=30) | 8(32.0) | 6.0(6.0,7.0) | 13.0(11.8,14.0) |
| Z值 | — | 3.646 | 4.185 |
| P值 | 0.004 | 0.001 | <0.001 |
表3 模块组与对照组术中并发症发生情况比较Table 3 Comparison of intraoperative complications between the module group and the control group |
| 组 别 | 例数 | 并发症/n | 无/n | 发生率/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一过性神经损伤 | 硬膜撕裂 | 血管损伤 | 脏器损伤 | 其他 | ||||
| 模块组 | 30 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 3.3 |
| 对照组 | 30 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27 | 10.0 |
| P值 | 0.605a | |||||||
| 注:aFisher确切概率法。 |
表4 模块组与对照组术康复情况比较Table 4 Comparison of operative rehabilitation between the module group and the control group M(P25 , P75) |
| 组 别 | 模块组 | 对照组 | Z值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS评分/分 | ||||
| 术前 | 7.0(7.0,8.0) | 7.0(6.0,7.2) | 1.052 | 0.293 |
| 术后3个月 | 1.5(1.0,2.2)a | 2.0(1.0,2.0)a | 0.211 | 0.833 |
| 术前术后评分差值 | 5.0(4.8,6.2) | 5.0(3.0,5.0) | 3.106 | 0.002 |
| ODI评分/分 | ||||
| 术前 | 43.5(41.0,45.0) | 43.5(41.8,45.0) | 0.060 | 0.952 |
| 术后3个月 | 11.0(10.0,12.0)a | 12.0(11.0,12.2)a | 1.749 | 0.080 |
| 术前术后评分差值 | 32.5(30.0,33.2) | 32.0(31.0,33.0) | 0.924 | 0.355 |
| 注: 与术前相比, aP < 0.01。 |
| [1] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [2] |
A prospective, cohort evaluation of 262 consecutive patients who underwent transforaminal endoscopic excision for recurrent lumbar disc herniation, after previous discectomy.To review complications and results of the endoscopic transforaminal discectomy (ETD) for recurrent herniated disc with a 2-year follow-up.Recurrent herniation is a significant problem, as scar formation and progressive disc degeneration may lead to increased morbidity after traditional posterior reoperation. The studies published until now on recurrent disc herniation concern various operative techniques, mostly the lumbar microdiscectomy, which is still seen as the standard. The advantage of ETD could be that there is no need to go through the old scar tissue and the procedure can be performed in local anesthesia. The disadvantage may be a long learning curve for the surgeon.Between January 1994 and November 2002, 262 patients with primarily radicular problems underwent an ETD for a recurrent herniated disc. Two hundred and thirty-eight of these patients (90.84%) completed our 2-year follow-up questionnaire. Initial surgery of 82 patients was performed in-house, 180 external. Average age was 46.4 years. The female/male ratio was 29/71%.At 2-year follow-up 85.71% of patients rated the result of the surgery as excellent or good. 9.66% reported a fair and 4.62% patients an unsatisfactory result. Average improvement of back pain of 5.71 points and 5.85 points of leg pain on the VAS scale (1-10). According to Mac Nab, 30.67% of the patients felt fully regenerated, 50% felt their functional capacity to be slightly restricted, 16.81% felt their functional capacity noticeably restricted, and 2.52% felt unimproved or worse. All patients participated in a 3-month follow-up to establish the perioperative complications. The overall complication rate was 10/262 (3.8%), including 3 nerve root irritations and 7 early recurrent herniations (<3 month). There was no case of infection or discitis. After 3 months and within 2 years, 4 patients have been treated for a recurrent herniated disc in our own center and 7 patients have been treated elsewhere, resulting in a recurrence rate 11/238 (4.62%).ETD for recurrent disc herniation seems to be an effective method with few complications and a high patient satisfaction.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [3] |
崔冠宇, 舒雄, 刘亚军, 等. 经皮椎间孔镜下椎间盘切除治疗伴有高髂嵴的L5/S1椎间盘突出症[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(27): 4333-4338. DOI.org/10.12307/2021.192.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [4] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [5] |
曹正霖, 禤天航, 于淼, 等. 自制辅助定位穿刺装置在经皮椎间孔镜下髓核摘除术中的应用效果[J]. 广西医学, 2017, 39(9): 1320-1324. DOI: 10.11675/j.issn.0253-4304.2017.09.10.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [6] |
韩艳波, 吴月, 怡红玉, 等. 三轴直角坐标系立体定位CT导航辅助经皮椎间孔镜手术治疗腰椎间盘突出症的疗效分析[J]. 颈腰痛杂志, 2019, 40(4): 574-575.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7234.2019.04.053.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [7] |
胡安文, 吴博文. 靶点靶线体表投影穿刺法在侧路椎间孔镜技术中的应用[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2020, 26(3): 245-249. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6604.2020.03.013.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [8] |
王长昇, 陈荣生, 朱希田, 等. 混合现实技术导航联合椎间孔镜手术治疗腰椎间盘突出症应用研究[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2022, 21(3): 324-328. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2022.03.028.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [9] |
马维理, 陈国奋, 熋亮. 经皮椎间孔镜下腰间盘切除术中3D打印导航模板辅助穿刺的应用[J]. 颈腰痛杂志, 2021, 42(4):562-564. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7234.2021.04.036.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [10] |
刘维克, 夏乐, 杨同岗, 等. 骨科手术机器人在个体化椎间孔镜穿刺导向中的应用[J]. 颈腰痛杂志, 2020, 41(4): 389-391. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7234.2020.04.002.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [11] |
刘益雷, 范新成, 伊超凡, 等. 椎间孔镜技术新型体表定位器在经皮内镜腰椎间盘切除术中的应用[J/OL]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2021, 15(4): 260-264. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2021.04.005.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [12] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [13] |
曾月东, 苏建成, 谢伟, 等. 椎间孔镜靶向穿刺新技术治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2016, 22(3): 201-204, 241.DOI:10.13795/j.cnki.sgkz.2016.03.003.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [14] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [15] |
隆振学, 韦文, 王露瑶, 等. 经皮椎间孔镜定位穿刺技术及相关辅助导航设备应用的研究进展[J]. 右江医学, 2019, 47(7): 543-546. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1383.2019.07.016.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [16] |
巩陈, 吴建明, 张文志, 等. 三维可视化虚拟手术系统联合椎间孔定位穿刺器在经皮内镜下经椎间孔减压手术治疗腰椎管狭窄症中的应用[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2022, 8(24):3087-3094. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2022.24.012.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [17] |
This study aimed to construct a multi-segment lumbar finite element model (FEM) of PTED surgery to analyze the changes in stress and ROM after visible trephine-based foraminoplasty. The CT scans of a 35-year-old healthy male were used to develop a multi-segment lumbar FEM with Mimic, Geomagic Studio, Hypermesh and MSC.Patran. Different foraminoplasty was performed on the model, and these were grouped into normal group (A), the ventral resection group (B), the apex resection group (C), the ventral + apex + isthmus resection group (D), and the SAP + isthmus + lateral recess resection group (E). A vertical load of 500N and a torque of 10N·M were applied to the upper surface of the L3 vertebral body to simulate the biomechanical characteristics under the motion of flexion, extension, lateral bending, and rotation. The von Mises stress maps of the intervertebral f, vertebral body, facet joints, and the ROM of the L3-S1 intervertebral disk were calculated and analyzed. The changes of peak stress on the vertebral body for each group were not significant in the same motion state. Significant stress differences were observed in the L4/5 intervertebral disks, while no obvious stress changes were observed for the L3/4 and L5/S1 intervertebral disks. The stress of the L3/4 and L5/S1 facet joints decreased after L4/5 foraminoplasty, while the stress of L4/5 facet joints displayed an overall increasing trend. Significant asymmetrical stress changes of bilateral facet joints were observed in all three segments, particularly during bilateral rotation movements. The ROM of L3-S1 gradually increased from Group A to Group E, especially during flexion, left lateral bending, and right rotation, with the highest elevation observed for the L45 ROM. Our FEM indicated that enlarged resection and exposure of the articular surface could lead to significant asymmetrical stress changes in the bilateral facet joints and ROM instability of the surgical and adjacent segments. These findings suggested that unnecessary and excessive resection should be avoided in PTED to reduce the incidence of low back pain and the risk of postsurgical degeneration.© 2023. The Author(s).
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [18] |
During minimally invasive spine surgery, nerve root decompression is challenging due to the anatomical division and uncertainty in lumbar lateral recess (LLR).To evaluate the outcome and safety of foraminoplasty using percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic decompression (PTED) (performed with an aid of a trephine) in the treatment of lumbar lateral recess stenosis (LLRS).All operations were performed under local anesthesia and in prone position. The puncture point was 10-14 cm away from the midline of the spinous process. One hundred eight individuals with LLRS who underwent PTED from September 2016 to December 2020 in our hospital were enrolled in the study. Visual Analog Scale (VAS) and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) scores were collected preoperatively after 1 day, 7 days, 1 month and at the final follow-up (June 2021). Low back pain and leg pain were measured using VAS score. Functional outcomes were assessed with ODI and modified Macnab criteria.After the surgery, the VAS score and ODI were statistically significant at all follow-up points compared with the pre-surgery (both p < 0.05). Based on the modified Macnab scores at the final follow-up, the satisfaction rate at postoperative 1 month was 96.3% and the satisfaction rate at postoperative 7 days was 70.38%. A significant difference was observed between the 2 groups (p < 0.05).Foraminoplasty using PTED performed with a trephine is one of the safe and effective, minimally invasive methods to treat LLRS.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [19] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [20] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [21] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [22] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [23] |
李坚, 李锦锦, 何丽萍. 经皮椎间孔镜脊柱系统术治疗腰椎间盘突出症合并神经根管狭窄[J]. 中山大学学报(医学科学版), 2023, 44(2): 342-347. DOI: 10.13471/j.cnki.j.sun.yat-sen.univ(med.sci).2023.0220.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [24] |
楼亦文, 李琳, 陈潜. 腰部肌群稳定性康复训练结合肌内效贴扎技术在腰椎间盘突出症康复治疗中的应用[J]. 中山大学学报(医学科学版), 2024, 45(1): 152-160. DOI: 10.13471/j.cnki.j.sun.yat-sen.univ(med.sci).20240004.015.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [25] |
陆继业, 蒋国强, 卢斌, 等. Dynesys治疗老年腰椎退行性疾病的中远期临床对照研究[J]. 新医学, 2019, 50(2): 129-133. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9802.2019.02.011.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [26] |
王正基, 廖文波. 全内镜前路经椎体联合后路经椎板间隙治疗双节段颈椎间盘突出1例报告[J]. 遵义医科大学学报, 2023, 9(10): 998-1002.DOI: 10.14169/j.cnki.zunyixuebao.2023.0135.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [27] |
付至江, 刘宗超, 马川, 等. 独活寄生汤加减对改善肝肾亏虚型腰椎间盘突出症患者疼痛和焦虑的效果[J]. 西南医科大学学报, 2022, 45(3): 245-248. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-3351.2022.03.013.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [28] |
朱仲廉, 周平辉, 王照东, 等. MiR-206对腰椎间盘髓核细胞衰老、凋亡的调控机制[J]. 中华全科医学, 2024, 10(2): 209-211, 268. DOI: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.003367.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [29] |
刘智伟, 白晓亮, 孔亚荣, 等. PTED治疗对腰椎间盘突出症IL-6、HMGB-1、IL-17水平的影响[J]. 分子诊断与治疗杂志, 2024, 10(1): 149-152, 157.DOI:10.19930/j.cnki.jmdt.2024.01.029.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [30] |
程清平, 王东福, 焦朋, 等. 腰椎间盘突出症术后椎间隙感染的治疗及危险因素分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2017, 3(1):32-35.DOI:0.7531/j.issn.1672-9935.2017.01.009.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [31] |
马向伟. 腰椎间盘突出症术后并发椎间隙感染的处理措施及相关因素探讨[J]. 颈腰痛杂志, 2019, 40(1): 105-107. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7234.2019.01.038.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [32] |
介思, 赵祥鑫, 蔡立邦, 等. 腰痛解凝汤配合穴位针灸对腰椎间盘突出症患者的临床疗效及自身免疫水平的影响[J]. 四川中医, 2023, 41(12): 161-164. DOI: 10.19664/j.cnki.1002-2392.220024.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
 PDF(4966 KB)
PDF(4966 KB)
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |